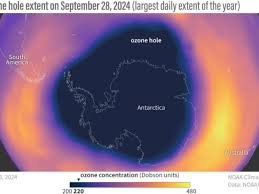
Since the recovery of the ozone layer began in 1992, the hole in the ozone layer of the affected atmosphere has become smaller.
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration has announced that this hole exists every year at the South Pole over Antarctica and is getting smaller than in previous years.
NOAA and NASA scientists estimate that the ozone layer will be fully recovered by 2066.
Paul Newman, leader of NASA’s ozone research team, said the 2024 Antarctic hole will be smaller than the ozone holes seen in the early 2000s.
“The gradual improvement we’ve seen over the past two decades shows that international efforts to curb ozone-depleting chemicals are working,” he added.